Yo, peeps! Let’s dive into the wild world of inflation, where prices go up and wallets cry. Buckle up as we unravel the mysteries of this economic rollercoaster ride with some serious swag.
So, what exactly is inflation and why should you care? Get ready to be schooled on the ins and outs of this money game.
What is Inflation?
Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of a currency. It is a key indicator of the health of an economy and is typically measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Causes of Inflation
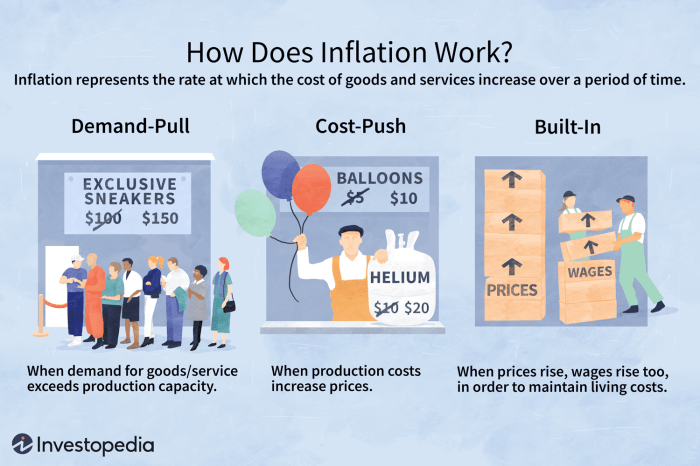
- 1. Demand-Pull Inflation: This type of inflation occurs when aggregate demand in an economy exceeds the available supply of goods and services, leading to a rise in prices.
- 2. Cost-Push Inflation: Cost-push inflation happens when the cost of production increases, causing producers to raise prices to maintain their profit margins.
Impact of Inflation
- Inflation impacts consumers by reducing the purchasing power of their money, meaning they can buy fewer goods and services with the same amount of money.
- Businesses are affected by inflation as it can lead to uncertainty in planning, higher costs of production, and potentially lower profit margins if they cannot pass on the increased costs to consumers.
Factors Influencing Inflation
Inflation is influenced by various factors that can impact the overall economy. Let’s dive into some key factors that play a significant role in shaping inflation rates.
Role of Central Banks in Controlling Inflation
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a crucial role in controlling inflation. Through monetary policy tools like interest rate adjustments and open market operations, central banks aim to stabilize prices and keep inflation in check. By carefully monitoring economic indicators and adjusting policy as needed, central banks work to maintain a healthy balance between growth and inflation.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The interaction of supply and demand in the economy can also impact inflation rates. When demand for goods and services outstrips supply, prices tend to rise, leading to inflation. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices may fall, resulting in deflation. Understanding these dynamics is essential for predicting inflation trends and making informed policy decisions.
Impact of Government Policies on Inflation
Government policies, such as fiscal stimulus packages and taxation measures, can have a direct impact on inflation. For example, increased government spending can boost demand in the economy, potentially leading to higher inflation. On the other hand, austerity measures may dampen demand and inflation rates. By implementing appropriate policies, governments can influence inflation levels and promote economic stability.
Measuring Inflation
Inflation is a crucial economic indicator that affects the purchasing power of consumers and the overall economy. Various methods are used to measure inflation, providing valuable insights into price changes over time.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is one of the most commonly used methods to measure inflation. It tracks the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time. By comparing the CPI from different periods, economists can calculate the inflation rate and understand how prices are changing in the economy.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
On the other hand, the Producer Price Index (PPI) measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers for their goods and services over time. This index helps to gauge inflationary pressures at the wholesale level, providing insights into potential future price changes for consumers.
Significance of Inflation Rates in Economic Indicators
Inflation rates play a significant role in economic indicators as they reflect the overall health of the economy. A moderate level of inflation is generally considered healthy for economic growth, while high inflation can erode purchasing power and lead to economic instability. Central banks closely monitor inflation rates to make informed decisions on monetary policy and interest rates.
Examples of Calculating and Interpreting Inflation Rates
To calculate inflation rates, economists compare the CPI or PPI from different time periods and calculate the percentage change. For example, if the CPI was 100 in the base year and 110 in the current year, the inflation rate would be calculated as follows:
(Current CPI – Base CPI) / Base CPI x 100
Interpreting inflation rates involves understanding the impact on consumers, businesses, and the overall economy. High inflation rates may lead to higher interest rates, affecting borrowing costs for individuals and businesses. Conversely, deflation, or negative inflation, can signal economic downturns and decreased consumer spending.
Effects of Inflation
When inflation strikes, it can have a significant impact on various aspects of the economy, affecting both individuals and businesses. Let’s dive into how inflation influences purchasing power, standard of living, interest rates, savings, and strategies to hedge against it.
Purchasing Power and Standard of Living
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. As prices rise, each dollar buys fewer goods and services, leading to a decrease in real income. This can ultimately lower the standard of living for individuals and families, making it harder to afford the same level of goods and services as before.
Interest Rates and Savings
Inflation can also impact interest rates, as central banks may raise rates to combat rising prices. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, affecting individuals with loans or mortgages. On the other hand, savers may see lower real returns on their savings due to inflation outpacing interest rates, reducing the value of their savings over time.
Strategies to Hedge Against Inflation
To protect against the negative effects of inflation, individuals and businesses can employ various strategies. Investing in assets that tend to increase in value with inflation, such as real estate, commodities, or stocks, can help preserve wealth. Diversifying investments, using inflation-indexed securities, and adjusting pricing strategies for businesses can also mitigate the impact of rising prices.